- formatting
- images
- links
- math
- code
- blockquotes
- external-services
•
•
•
•
•
•
-
Building Intelligent Agents for Connect-4: Tree Search Algorithms
Learn how the Alpha-Beta search algorithm optimizes Minimax for Connect-4 by pruning unnecessary branches, improving efficiency, and enabling stronger gameplay strategies.
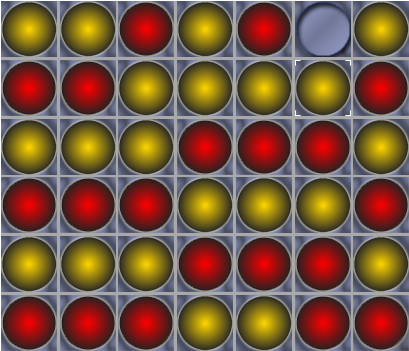
-
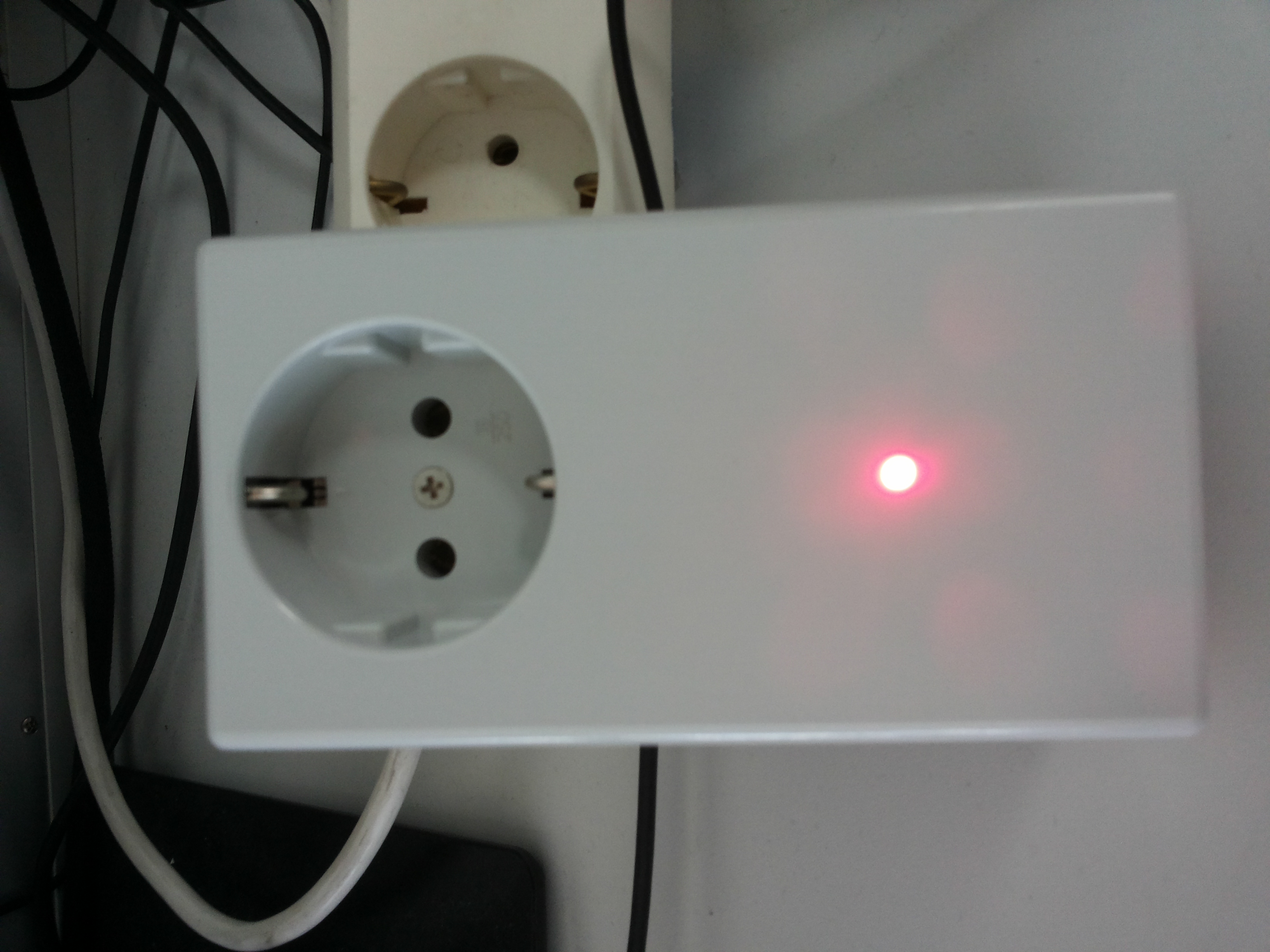
DIY IoT: Building a Smart Adapter Plug from Scratch with ESP8266-01 and MQTT
A DIY IoT project using the ESP8266-01 module to build a network-controlled adapter plug from scratch. This project demonstrates how to create connected devices with minimal hardware and effort using Wi-Fi and MQTT.

-
Seychelles from Above: A Drone Journey Across Its Most Beautiful Beaches
Discover the Seychelles’ most stunning beaches from a new perspective. From the iconic Anse Source d’Argent on La Digue to the sweeping Anse Intendance on Mahé, these drone shots capture some of the islands’ breathtaking beauty.

-
Short Notes: Understanding Euclid’s GCD Algorithm
A concise walkthrough of why Euclid’s Algorithm correctly computes the greatest common divisor (GCD), using basic properties of divisibility and remainders.
-
Conway's Game of Life
An introduction to Conway’s Game of Life with an implementation in R. We explore the simple rules behind this zero-player cellular automaton, simulate its evolution on a 100×100 grid, and visualize emerging patterns and population dynamics over time.
