- formatting
- images
- links
- math
- code
- blockquotes
- external-services
•
•
•
•
•
•
-
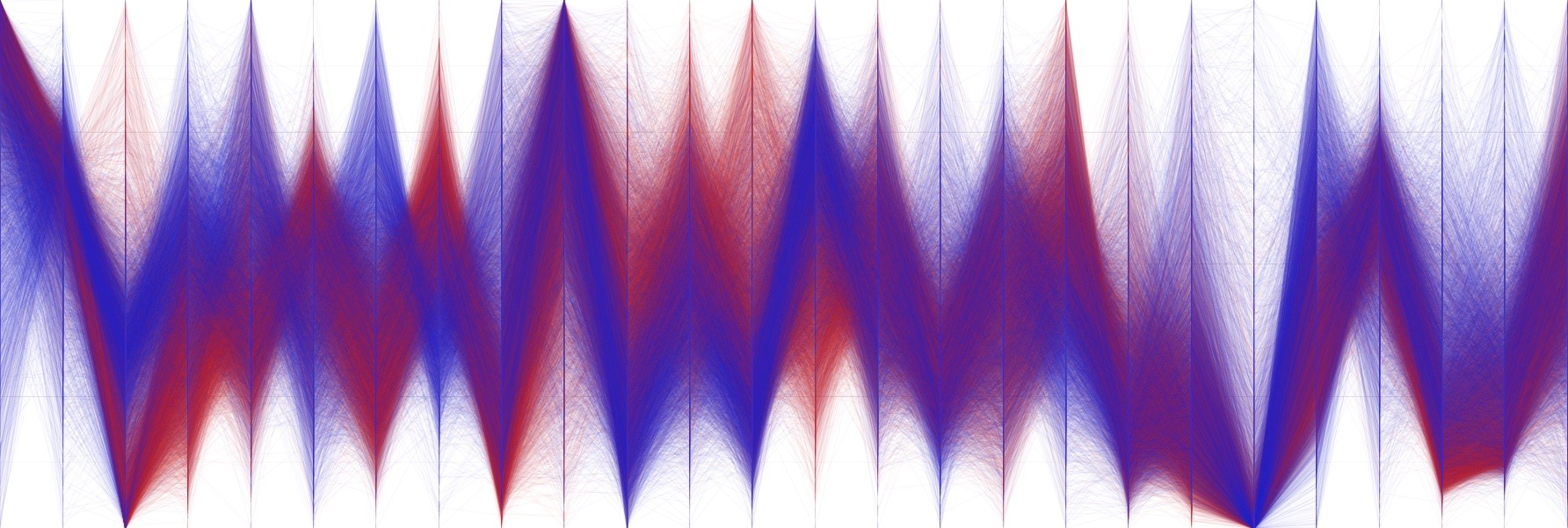
Visualizing High-Dimensional Data Using Parallel Coordinates
A deep dive into the visualization technique of Parallel Coordinates (||-Coordinates), exploring its strengths, challenges, and practical applications in data mining. Through detailed case studies—including wine quality analysis and the MiniBooNe particle dataset—we demonstrate how this powerful tool can reveal hidden structures, correlations, and clusters in high-dimensional data. With insights into alpha blending, axis reordering, outlier handling, and visual classification, this post offers both theoretical background and hands-on use cases for using Parallel Coordinates effectively.
-
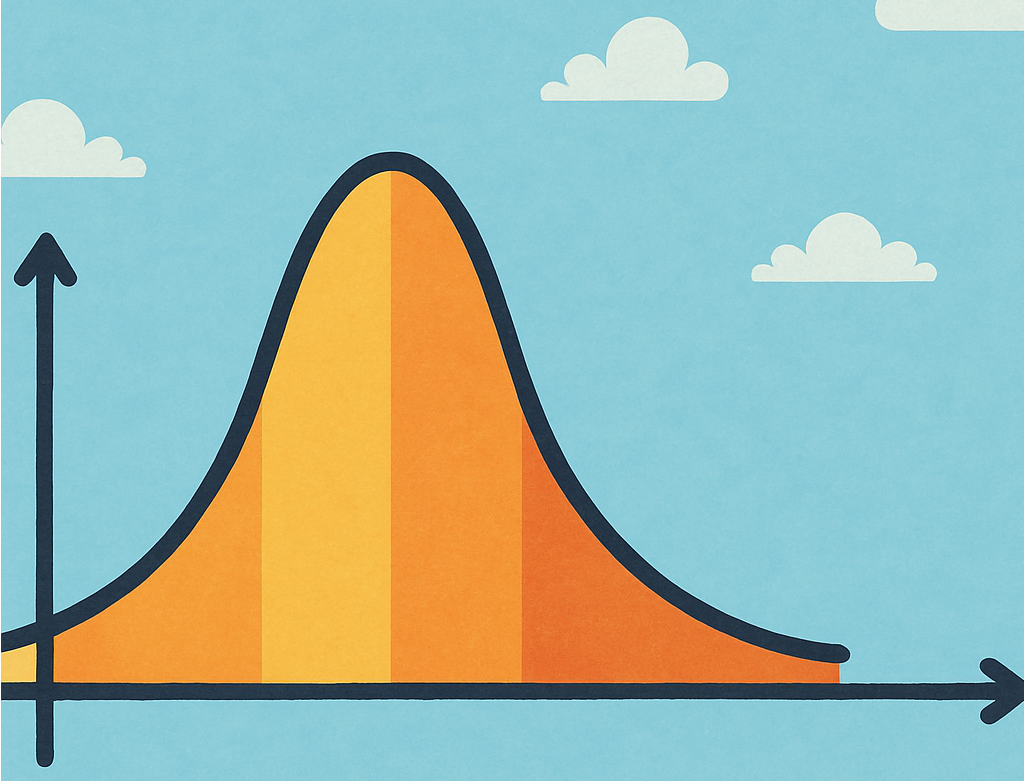
Short Notes: The Multivariate Gaussian Distribution With a Diagonal Covariance Matrix
This post explores how a multivariate Gaussian distribution simplifies when the covariance matrix is diagonal. By breaking down the math, we show how the density function factorizes into a product of independent univariate Gaussians—making both interpretation and computation more tractable.
-
Building Intelligent Agents for Connect-4: First Steps
A deep dive into the construction of intelligent agents for Connect-4. This introductory post covers the historical context, motivation, complexity of the game, and foundational concepts behind AI-based approaches—particularly tree search and reinforcement learning methods. Includes a preview of the full 7-part series and links to an open-source Python3/C++ framework.
-
Understanding Bootstrap Sampling: Where Euler’s Number Meets Random Forests
A common problem involves drawing a sample of size n from a set of n elements, with replacement. For example, in Random Forests, each decision tree is trained on a bootstrap sample drawn n times with replacement from the training data. A natural question is: how many unique examples can we expect in such a sample? Since sampling is done with replacement, some examples are likely selected multiple times, while others may not be selected at all.

-
Beyond 3D: Generalizing the Vector Cross Product
Imagine you are working in three-dimensional space and have two directions. You want to find a third direction that is perpendicular to both of them. In this setting, there's a well-known solution: the cross product. When applied to the two original directions, it produces a new one that is exactly orthogonal to both.